The team of Professor Feng Wei from Tianjin University in China has developed a self-propelled soft robot that can roam on its own through 4D printing technology.
This tubular robot is made of a material called liquid crystal elastomer. It assembles itself when exposed to heat. It has unfettered movement capabilities and does not require any other processing procedures. This robot rolls smoothly and powerfully, and its speed and direction can be adjusted by changing its shape and size. Moreover, the intelligent response behavior of robots constitutes machine perception based on artificial intelligence. The research results were published in Matter, the top journal of Cell Press.
(Tactile perception process/ via Tianjin University)
3D printing can automatically and accurately transform design ideas into complex parts based on digital models. It is one of the best choices for manufacturing soft robots. 4D printing technology is created by combining 3D printing with new engineering smart materials. Simulate autonomous objects. These objects have a dynamic structure with various stimulus-response behaviors. In addition to simple deformation, 4D printed intelligent software robots with perceptual ability and adaptability can also be produced.
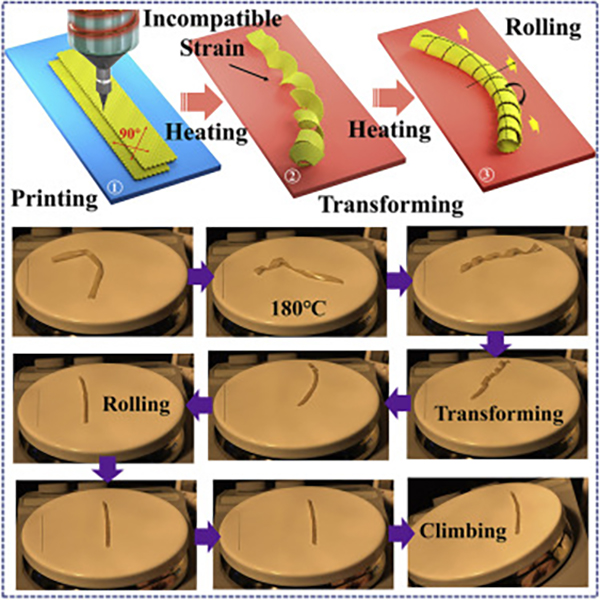
Professor Feng Wei’s team 3D printed a flat rectangular liquid crystal elastomer sheet and heated the surface below it to 160°C or higher. At this temperature, the heat from the surface below causes the robot to twist itself, forming a small tube shape similar to a coil spring. Further contact with the heated surface creates strain in the material, causing it to roll on its own through peristaltic motion. After printing, the shape changes according to the heat, causing the device to start 4D printing. At this time, the fourth dimension of time is added to the equation.
(Tactile perception process / via Tianjin University)
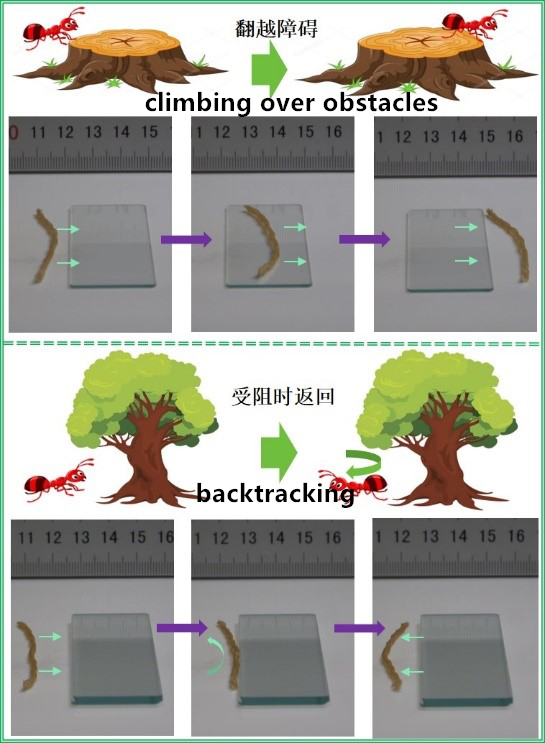
The entire driving process of the tubular robot is automatic, and the task can be completed without changing the environmental factors without manual control. The rolling speed of the longer sample is faster than that of the shorter sample. Since the sample exhibits certain viscoelastic properties and considerable rolling driving force, when the sample is placed on an inclined heating plate at a certain angle, the sample can still be rolled up.
“We processed liquid crystal elastomers into samples of various shapes through 4D printing, and stimulated these samples with light, heat, and electricity to observe their responses,” added Professor Feng Wei. “In addition to deformation, we also found many interesting driving phenomena.”
In terms of future applications, researchers from Tianjin University hope to see their soft robots work in narrow spaces such as pipes or under extreme conditions above 200°C, instead of being limited to simple actuators, they can only work in fixed The position changes shape.
Post time: Oct-15-2021
