What Is 3D Printing?
3D printing, also called Additive Manufacturing, is an innovative technology that enables you to create a physical 3D object from a digital model. It started in the 80’s under the name ‘rapid prototyping’ because this was the purpose of this technology: to prototype cheaper and faster. However, a lot has changed since then, and today 3D printers offer amazing results and allow you to create almost anything you can imagine.
How Does 3D Printing Work?
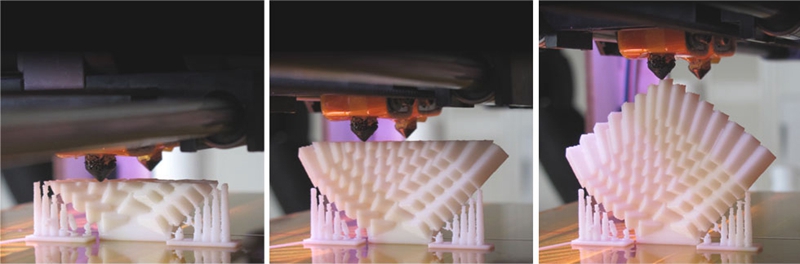
Every 3D printer builds parts based on the same primary principle: a digital model is turned into a physical 3D object by adding material layer after layer. This is where the alternative term Additive Manufacturing derives from.
3D printing is a fundamentally different way of creating parts compared to traditional subtractive (CNC Machining) or formative (Injection Molding) manufacturing technologies. No special tools are needed in 3D printing (for instance, a cutting tool with certain geometry or a mold). Instead the part is manufactured directly onto the built platform layer-by-layer.
The process always starts with a digital 3D model – the blueprint of the physical object. This model is sliced by the printer’s software into thin, two-dimensional layers and then turned into a set of instructions in machine language (G-code) for the printer to execute.
From here, the way a 3D printer works varies by process. For instance, desktop FDM printers melt plastic filaments and lay it down onto the build platform via a nozzle (like a high-precision, computer-controlled glue gun). Large industrial SLS machines melt (or sinter) thin layers of metal or plastic powders with the use of a laser.
The available materials vary by process as well. Plastics are by far the most common, but metals can be 3D printed as well. The produced parts can also have a wide range of specific physical properties, ranging from optically clear to rubber-like objects.
Depending on the dimension of the part and the type of printer, a print usually takes approximately 4 to 18 hours to complete. 3D printed parts are seldom ready-to-use out of the machine though. They often need some post-processing to achieve the desired level of surface finish. These steps take extra time and (usually manual) effort.
The possibilities of 3D printing are endless, and 3D printers are now becoming a commonplace tool in fields like product design, engineering, manufacturing, education and architecture.
Post time: Jan-02-2019