Flexible filaments are made of Thermoplastic Elastomer (TPE) which is a blend of hard plastic and rubber. As its name suggests, this material is elastic in its very nature, which allows the plastic to be flexed and stretched easily, and is widely used in a number of manufacturing processes for both consumer and industrial use. There are several types of TPE, with Thermoplastic Polyurethane (TPU) being the most commonly used among 3D printer filaments. The degree of its elasticity depends on the type of TPE and the chemical formulation used by the manufacturer. This article will introduce you 5 easy tips on how to print with flexible filament.
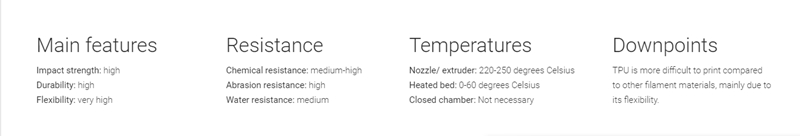
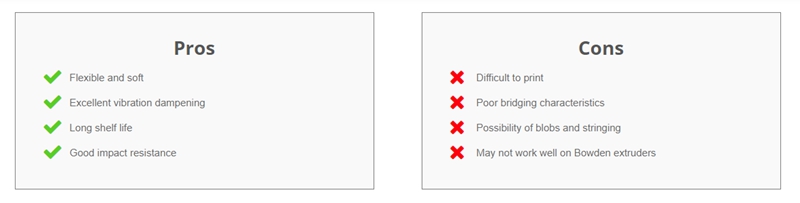
TPU material has a number of attributes, which make it an ideal choice for a wide range of applications. It is resistant to abrasion, oil, chemical and wearing, making it perfect for use in industries such as the automotive industry. Unlike other stiffer thermoplastic, TPU has features that include flexibility and conformity. It also has an excellent inter-layer adhesion and no curling or delamination during the 3D printing process, when using the correct settings.
(Source: Simplify3D)
5 Easy Tips for Successful Results with Flexible Filament
1. Use Slow and Consistent Feed Rates
It is often best to use slow and consistent feed rates when 3D printing with flexible filaments. This is due to the fact that the material is elastic in nature and can become uncontrollable if there are any sudden changes to the print speed. Higher print speeds can cause the filament to compress and will probably result in a jam. Finding the optimal print speed for flexible TPU filament can take several attempts based on trial and error, however, a good starting point is a speed between 30 – 40mm/s.
2. Use a Direct Drive Extruder
According to Fenner Drives, Bowden extruders are not recommended for printing with flexible filament. Though some partially flexible filaments work fine with Bowden extruders, most fully flexible filaments require Direct Drive extruders for optimal results. The distance between the drive gear and the melt zone of the hot-end needs to be as short as possible to efficiently feed the filament into the nozzle. Moreover, the pathway through which the filament travels into the melt zone should have tight tolerances to prevent the filament from kinking or coiling inside. Due to these factors, it is typically much easier to print flexible filaments with a Direct Drive extruder instead of a Bowden extruder.
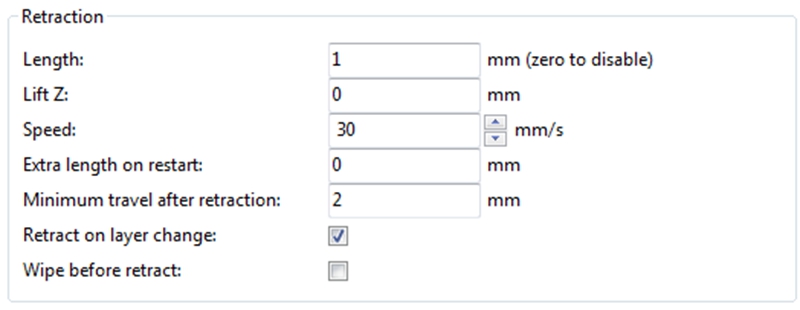
3. Optimize the Retraction Settings
Since TPU material is elastic and flexible, this makes it very sensitive to fast movements such as retractions. Therefore, for successful results when 3D printing with TPU filament, it is crucial that you optimize the retraction settings to limit the movements. You may adjust your retraction settings depending on the problem you are experiencing. If your extruder is clogged, you will want to lower your retraction. If you are experiencing additional material coming out of your nozzle, you will want to increase your retraction distance or speed.
4. Adjust Hot Bed Temperature & Use Tape
Flexible filament should stick pretty well to Kapton tape or regular Blue Painter’s tape. For your hot bed, temperature settings may vary depending on what type of printer and filament you are using. Most manufacturers recommend between 40-60 degree Celsius, however, for the best results, we recommend referring to your filament guide and make several attempts based on trial and error.
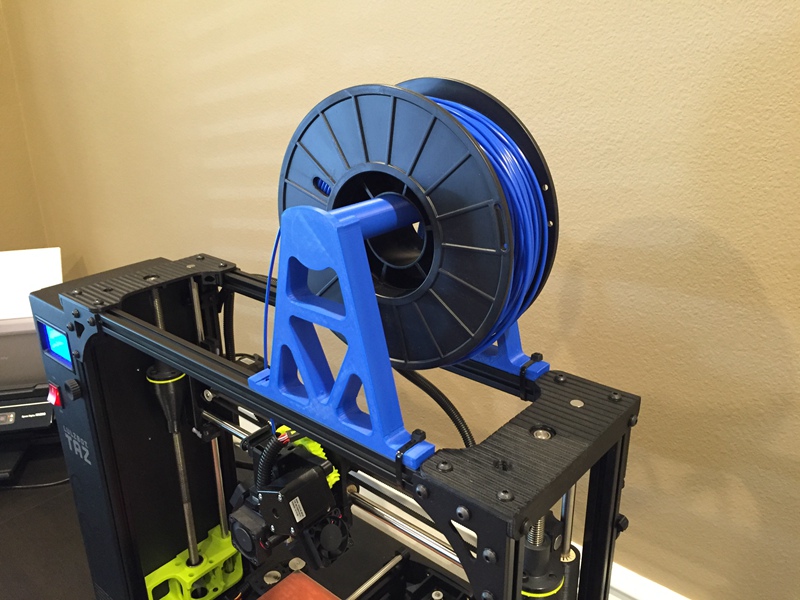
5. Reduce Resistance from Filament Spool
When it comes to 3D printing with TPU filament, a couple of tweaks to the filament spool can make a huge difference. Commonly, the extruder drive wheel will pull the filament into the nozzle, which results in the filament spool unwinding a small amount of plastic in this process. However, since TPU is flexible and elastic, the filament will be stretched while pulled which can actually lead to under-extrusion. Therefore, mount the spool above your printer so the filament unwinds downwards which can reduce any resistance.
To summarize the possibilities of flexible filament: objects printed from flexible filament are a better fit for practical use rather than for printing beautiful models. However, flexible materials can open completely new possibilities for your 3D printer. We hope the above-mentioned 5 easy tips on how to print flexible filament will help you overcome possible issues and you’ll end up printing something awesome. Happy 3D printing!
Post time: Mar-25-2019